Data Transformation with dbt
Step 1: Install the libraries
requirements.txt
dbt-core==1.2.0
dbt-postgres==1.1.1
psycopg2-binary==2.9.3
ipython-sql==0.4.1
boto3==1.24.31
Use the following shell command to install the libraries:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Extract and Load
In this part, we extract the data from the NYC Taxi website and load into postgres.
# dataset 1 - getting a sample of 1000 records for faster processing
yellow_tripdata_df =pd.read_parquet("https://d37ci6vzurychx.cloudfront.net/trip-data/yellow_tripdata_2022-05.parquet").sample(1000)
# select only few columns that we are interested in
yellow_tripdata_df = yellow_tripdata_df[['VendorID', 'tpep_pickup_datetime', 'tpep_dropoff_datetime', 'passenger_count', 'PULocationID', 'DOLocationID', 'fare_amount']]
# rename the columns
yellow_tripdata_df.columns = ['vendor_id', 'pickup_datetime', 'dropoff_datetime', 'passenger_count', 'pickup_location_id', 'dropoff_location_id', 'fare_amount']
# dataset 2
lookup_zone = pd.read_csv('https://d37ci6vzurychx.cloudfront.net/misc/taxi+_zone_lookup.csv')
# rename the columns
lookup_zone.columns = ['locationid','borough','zone','service_zone']
# Setup the credentials
def get_secret(secret_name):
region_name = "us-east-1"
session = boto3.session.Session()
client = session.client(
service_name='secretsmanager',
region_name=region_name)
get_secret_value_response = client.get_secret_value(SecretId=secret_name)
get_secret_value_response = json.loads(get_secret_value_response['SecretString'])
return get_secret_value_response
db_credentials = get_secret(secret_name='wysde')
USERNAME = db_credentials["RDS_POSTGRES_USERNAME"]
PASSWORD = db_credentials["RDS_POSTGRES_PASSWORD"]
HOST = "database-1.cy8ltogyfgas.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com"
PORT = 5432
DBNAME = "sparsh"
CONN = f"postgresql://{USERNAME}:{PASSWORD}@{HOST}:{PORT}/{DBNAME}"
# load the data into our postgres database
alchemyEngine = create_engine(CONN, pool_recycle=3600);
postgreSQLConnection = alchemyEngine.connect();
DBT_SCHEMA = "dbt_taxi"
lookup_zone.to_sql('taxi_zone_lookup', postgreSQLConnection, if_exists='replace', schema=DBT_SCHEMA, index=False)
yellow_tripdata_df.to_sql('yellow_taxi_trips', postgreSQLConnection, if_exists='replace', schema=DBT_SCHEMA, index=False);
postgreSQLConnection.close();
Validate the load:
%reload_ext sql
%sql {CONN}
%sql select * from {DBT_SCHEMA}.yellow_taxi_trips limit 10;
%sql select count(*) from {DBT_SCHEMA}.yellow_taxi_trips;
%sql select * from {DBT_SCHEMA}.taxi_zone_lookup limit 10;
%sql select count(*) from {DBT_SCHEMA}.taxi_zone_lookup;
Step 2: Setup the dbt project
This command will create a dbt project named nyctaxi:
dbt init nyctaxi
%cd nyctaxi
Step 3: Design the models
Staging Schema
./models/staging/schema.yml
version: 2
sources:
- name: source
schema: dbt_taxi
tables:
- name: yellow_taxi_trips
- name: taxi_zone_lookup
models:
- name: taxi_zone_lookup_model
description: "A list of all taxi zones with codes in NYC"
columns:
- name: locationid
tests:
- not_null
- name: borough
tests:
- not_null
- name: zone
tests:
- not_null
- name: service_zone
tests:
- not_null
- name: yellow_taxi_trips_models
description: "A reduced version of yellow taxi trip data in NYC"
columns:
- name: vendor_id
tests:
- not_null
- accepted_values:
values: ['1', '2', '4']
- name: pickup_datetime
tests:
- not_null
- name: dropoff_datetime
tests:
- not_null
- name: passenger_count
tests:
- not_null
- name: pickup_location_id
tests:
- not_null
- name: dropoff_location_id
tests:
- not_null
- name: fare_amount
tests:
- not_null
Staging model 1
./models/staging/yellow_taxi_trips_models.sql
select
vendor_id,
pickup_datetime,
dropoff_datetime,
passenger_count,
pickup_location_id,
dropoff_location_id,
fare_amount
from {{ source('source', 'yellow_taxi_trips') }}
Staging model 2
./models/staging/taxi_zone_lookup_model.sql
select
locationid,
borough,
zone,
service_zone
from {{ source('source', 'taxi_zone_lookup') }}
Serving schema
./models/schema.yml
version: 2
models:
- name: trips_with_borough_name
description: "Combines taxi rides with the borough names for pickup and dropoff locations."
columns:
- name: vendor_id
- name: pickup_datetime
- name: dropoff_datetime
- name: pickup_borough
- name: dropoff_borough
- name: passenger_count
- name: fare_amount
Serving model 1
We will now create another dbt model, which combines data from the two staging models. Let's assume we want to write a query to join the staging tables on the location ID fields and add the actual location names to the pickup and dropoff locations of the taxi ride data.
./models/trips_with_borough_name_model.sql
select
t.vendor_id,
t.pickup_datetime,
t.dropoff_datetime,
z1.borough as pickup_borough,
z2.borough as dropoff_borough,
t.passenger_count,
t.fare_amount
from {{ ref('yellow_taxi_trips_models') }} t
left join {{ ref('taxi_zone_lookup_model') }} z1
on t.pickup_location_id = z1.locationid
left join {{ ref('taxi_zone_lookup_model') }} z2
on t.dropoff_location_id = z2.locationid
Step 4: Run the models
dbt run
The output will be like this:
[0m02:52:30 Running with dbt=1.2.0
[0m02:52:31 [[33mWARNING[0m]: Did not find matching node for patch with name 'trips_with_borough_name' in the 'models' section of file 'models/schema.yml'
[0m02:52:31 Found 5 models, 4 tests, 0 snapshots, 0 analyses, 245 macros, 0 operations, 0 seed files, 2 sources, 0 exposures, 0 metrics
[0m02:52:31
[0m02:52:40 Concurrency: 1 threads (target='dev')
[0m02:52:40
[0m02:52:40 1 of 5 START table model dbt_taxi.my_first_dbt_model ........................... [RUN]
[0m02:52:44 1 of 5 OK created table model dbt_taxi.my_first_dbt_model ...................... [[32mSELECT 2[0m in 4.12s]
[0m02:52:44 2 of 5 START view model dbt_taxi.taxi_zone_lookup_model ........................ [RUN]
[0m02:52:48 2 of 5 OK created view model dbt_taxi.taxi_zone_lookup_model ................... [[32mCREATE VIEW[0m in 3.71s]
[0m02:52:48 3 of 5 START view model dbt_taxi.yellow_taxi_trips_models ...................... [RUN]
[0m02:52:52 3 of 5 OK created view model dbt_taxi.yellow_taxi_trips_models ................. [[32mCREATE VIEW[0m in 3.95s]
[0m02:52:52 4 of 5 START view model dbt_taxi.my_second_dbt_model ........................... [RUN]
[0m02:52:55 4 of 5 OK created view model dbt_taxi.my_second_dbt_model ...................... [[32mCREATE VIEW[0m in 3.72s]
[0m02:52:55 5 of 5 START view model dbt_taxi.trips_with_borough_name_model ................. [RUN]
[0m02:52:59 5 of 5 OK created view model dbt_taxi.trips_with_borough_name_model ............ [[32mCREATE VIEW[0m in 3.51s]
[0m02:53:02
[0m02:53:02 Finished running 1 table model, 4 view models in 0 hours 0 minutes and 31.09 seconds (31.09s).
[0m02:53:02
[0m02:53:02 [32mCompleted successfully[0m
[0m02:53:02
[0m02:53:02 Done. PASS=5 WARN=0 ERROR=0 SKIP=0 TOTAL=5
Step 5: Generate and analyze the docs
dbt docs generate
dbt also provides the facility to serve the doc site:
dbt docs serve
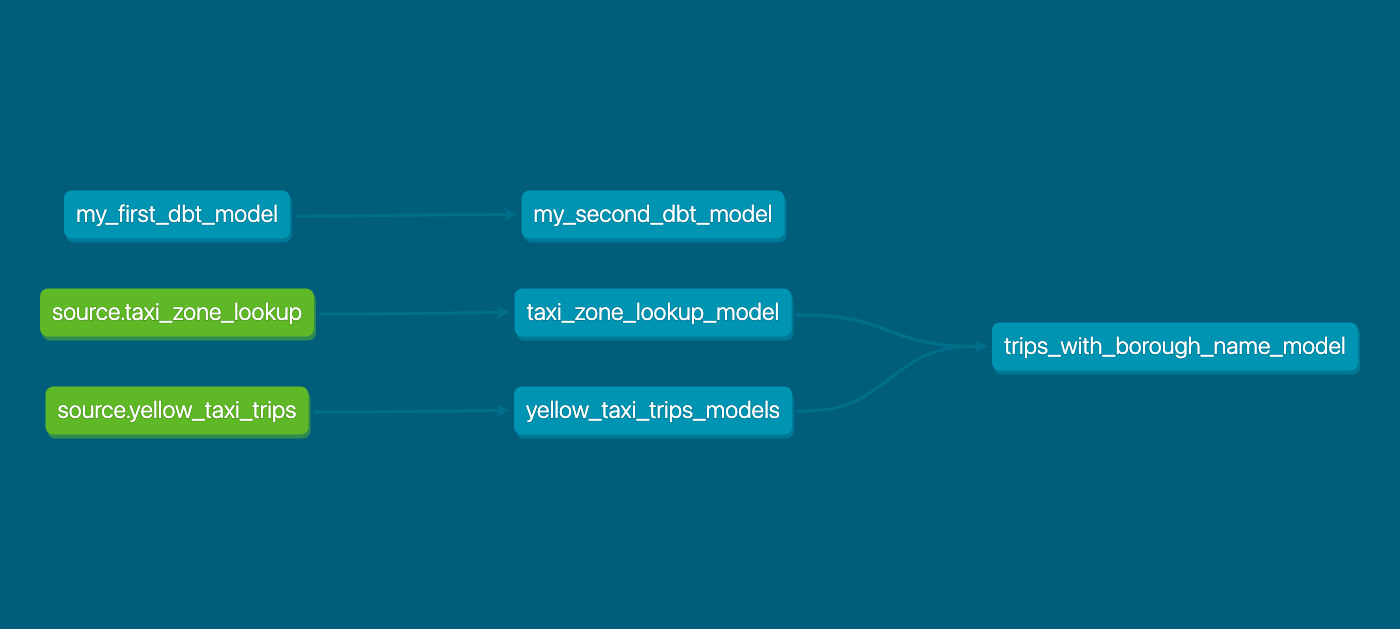
In the doc site, you will also find a lineage graph that will look like this: