Basics
What is Data Engineering?
The Data Engineering Ecosystem includes several different components. It includes disparate data types, formats, and sources of data. Data Pipelines gather data from multiple sources, transform it into analytics-ready data, and make it available to data consumers for analytics and decision-making. Data repositories, such as relational and non-relational databases, data warehouses, data marts, data lakes, and big data stores process and store this data. Data Integration Platforms combine disparate data into a unified view for the data consumers. You will learn about each of these components. You will also learn about Big Data and the use of some of the Big Data processing tools.
A typical Data Engineering lifecycle includes architecting data platforms, designing data stores, and gathering, importing, wrangling, querying, and analyzing data. It also includes performance monitoring and finetuning to ensure systems are performing at optimal levels. You will learn more about these systems with hands-on learning.
The first type of data engineering is SQL-focused. The work and primary storage of the data is in relational databases. All of the data processing is done with SQL or a SQL-based language. Sometimes, this data processing is done with an ETL tool. The second type of data engineering is Big Data–focused. The work and primary storage of the data is in Big Data technologies like Hadoop, Cassandra, and HBase. All of the data processing is done in Big Data frameworks like MapReduce, Spark, and Flink. While SQL is used, the primary processing is done with programming languages like Java, Scala, and Python.
Why we need Data Engineers?
Internet companies create a lot of data. Datasets are getting larger and messier in he internet era where there are large datasets for all the actions and interactions users make with your website all the way to product descriptions, images, time series info, comments etc.
It is said that data is the new oil. For natural oil, we also need a way to drill and mine this oil for it to be useful. In the same way, we need a way to mine and make sense of all this data to be useful.
On one had, there is a desire by executives and management to get insights from these datasets.
There is also a desire by data scientists and ML practitioners to have clean datasets to model with.
There are some really interesting trade-offs to make when you do this. And knowing about these can help you in your own journey as a data scientist or ML person working with large data. Irrespective of where you are in your data journey, I think you will find these interesting.
Roles in Data Teams
Data engineers are in the business of moving data—either getting it from one location to another or transforming the data in some man‐ ner. It is these hard workers who provide the digital grease that makes a data project a reality.
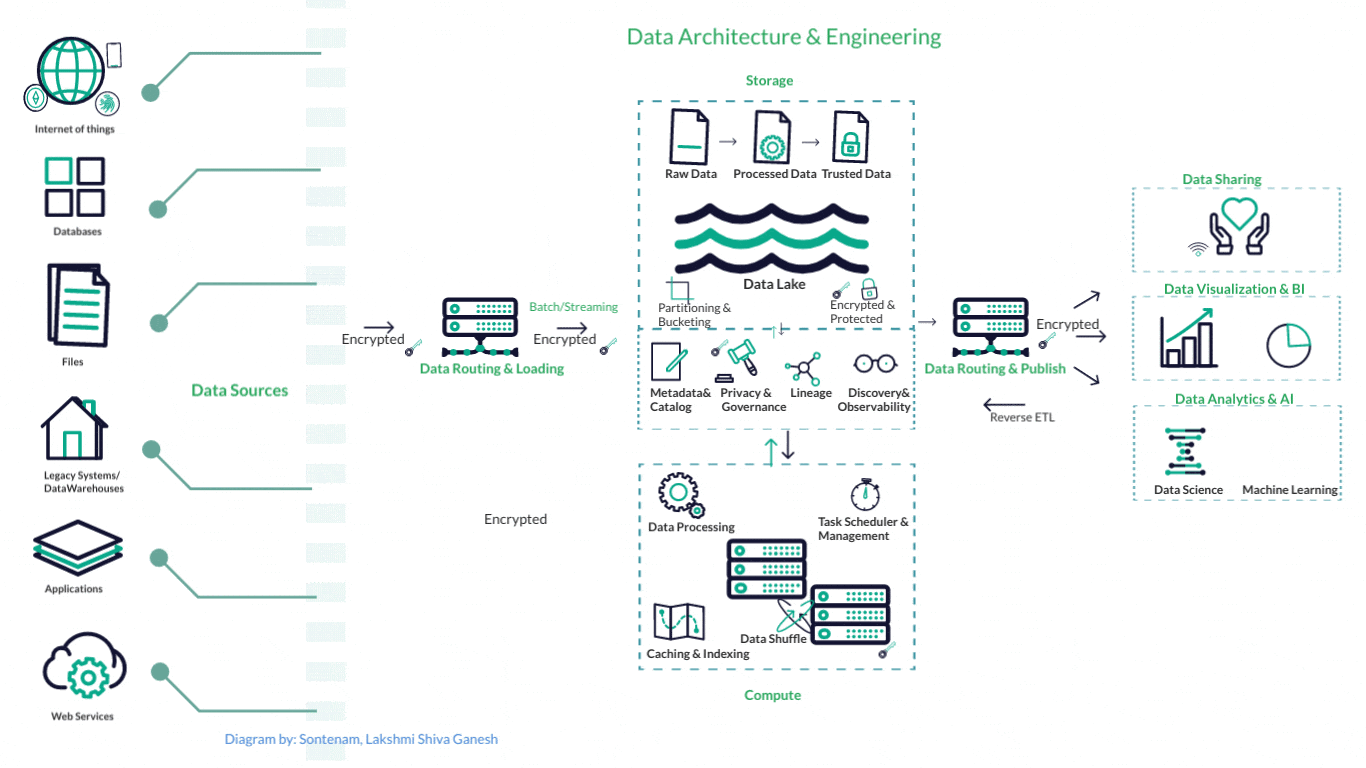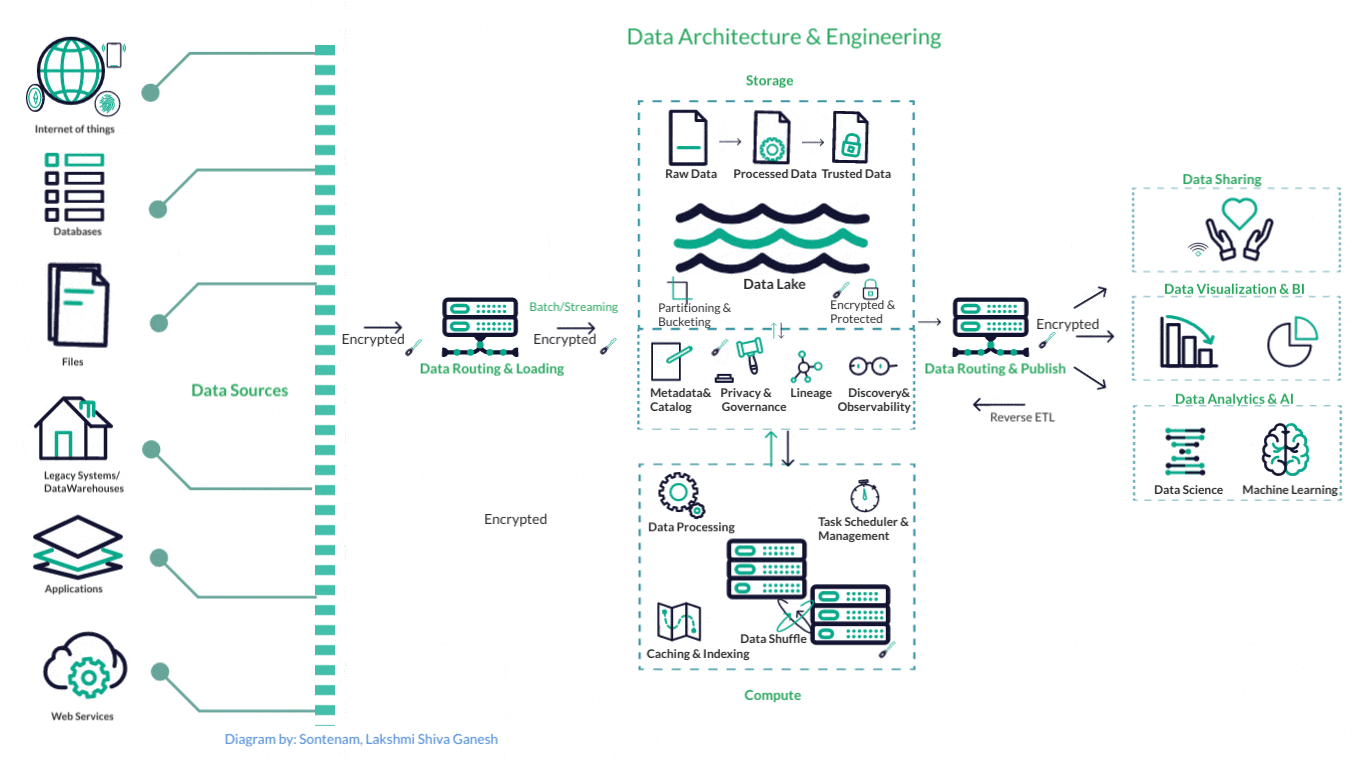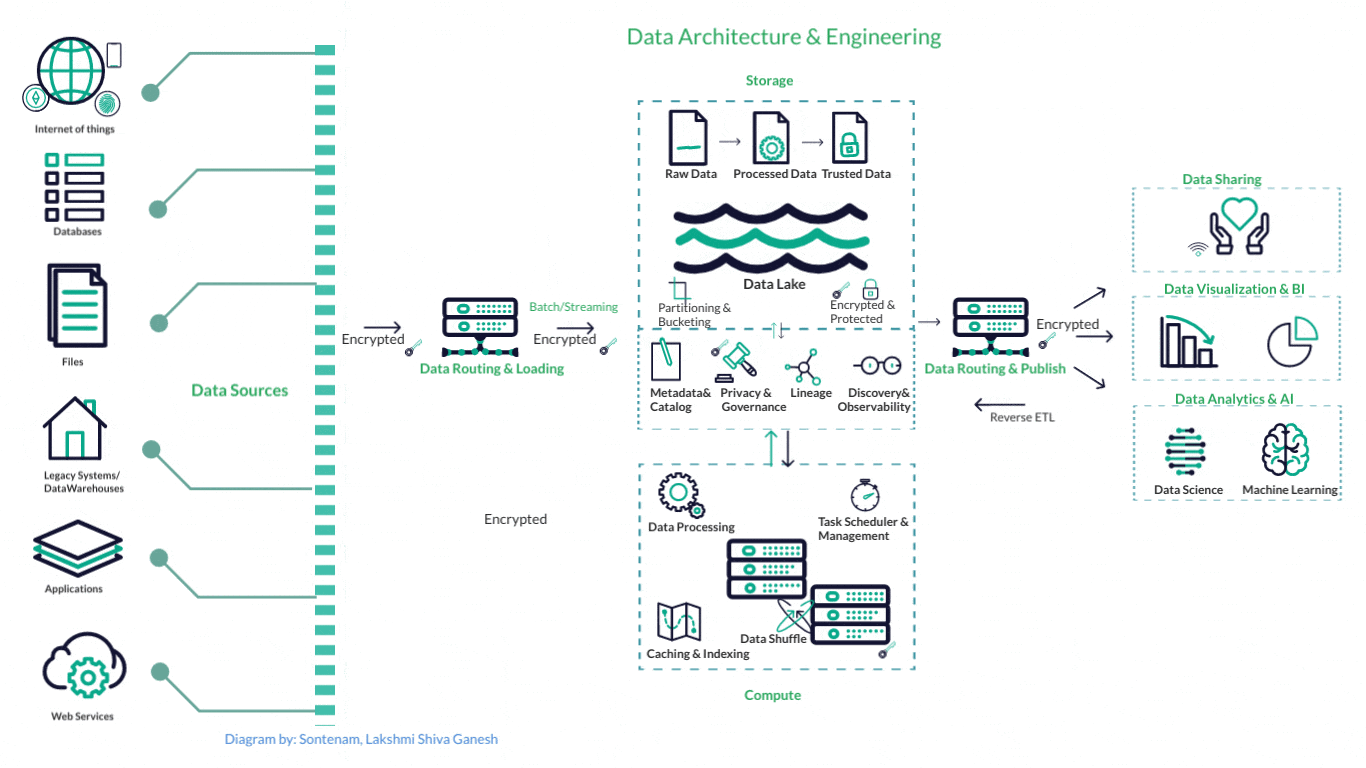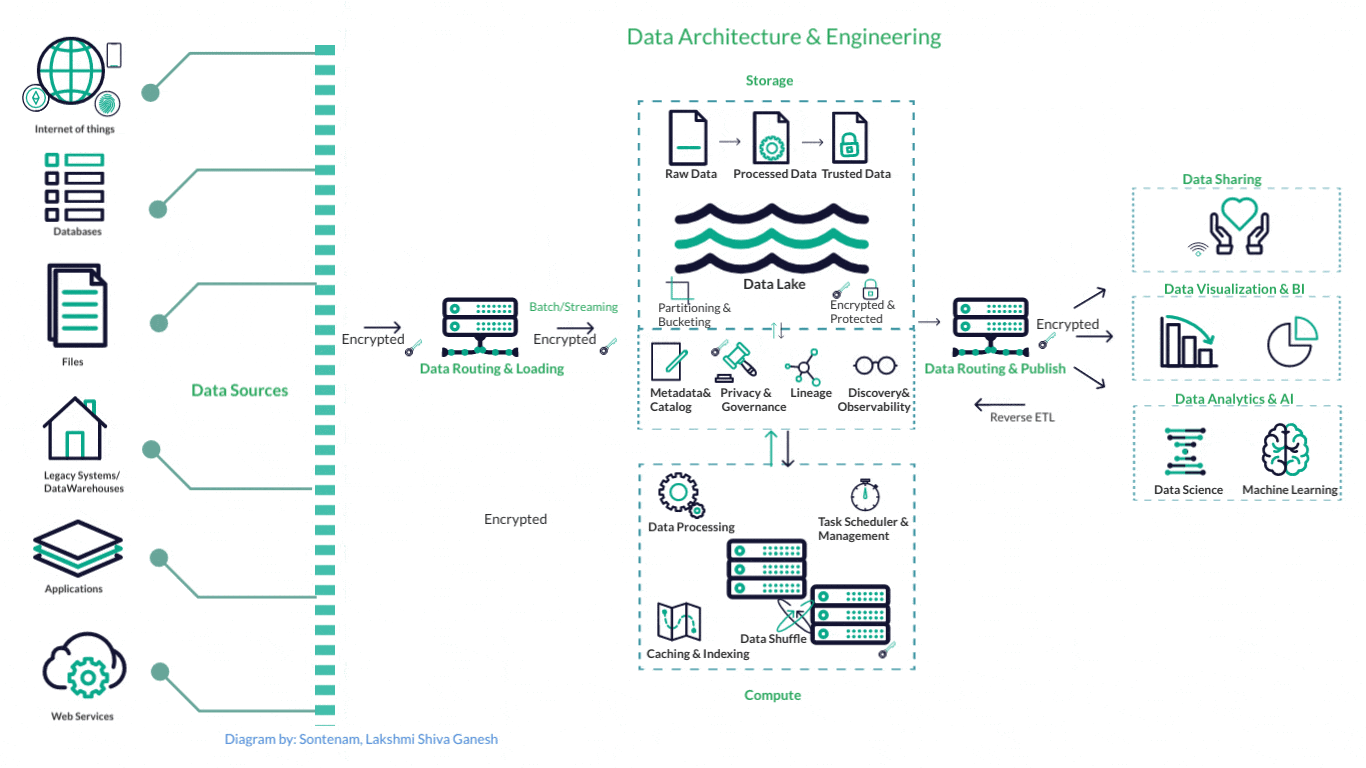
How a typical Data Engineering Pipeline looks
This is one example of a standard data pipeline in AWS ecosystem:

Know more about Data Engineering Basics
- Data Engineering Roadmap
- Approaching the data pipeline architecture
- The Data Engineering Megatrend: A Brief History
- How to gather requirements for your data project
- Five Steps to land a high paying data engineering job
Our Learning Framework
Learning
Learning will happen under the guided instructor-led sessions. We will do the following activites to learn the core concepts of data engineering:
- Theory and Case: We will find the answers to - 1) What is the particular technology/tool/concept is about, and 2) Why we are learnig about that? How things works in real-life is important and student should understand this very well. Along with the theory, we will also understand how companies/people uses the given technology/tool/concept in real-world to solve their business problems.
- Lab and Presentation: A guided session with instructur where instructor will show the process step-by-step in real-time and students will ask questions and clarify their doubts. Each lab will be broken down into steps after each step, each student will present that step in their own system/environment with some variations (if possible).
Assessment
Student assessment is the most important factor in tracking the progress of the students. We will do the assessment using the following methods and drills:
- Mock Interview (MI): This is a 1:1 mock interview between the instructor and the student. Student will be assessed based on the quality of responses.
- Peer Interview (PI): This is a 1:1 peer interview between a pair of students. Student will be assessed based on the quality of questions and quality of responses.
- Lab Assignment (LA): A hypothetical data engineering business case will be provided and the student has to apply the data engineering skills to solve the business requirement. Student will be assessed based on the assignment-specific factors and timely submission.
- Capstone Project (CP): Student will pick a brand/company persona and create a hypothetical scenario. Then the student will solve the scenario and submit the code for review. Student will be assessed based on the topic-specific factors and timely submission.
Every Week
- New Labs
- Full Mock Interviews
- Resume Buildups
- Essential Skill sessions
- Take-home Assignments
- Capstone Project Discussion
- Industrial Case Study Discussion
- General Discussion
Skills
SQL
Querying data using SQL is an essential skill for anyone who works with data.
Listed as one of the top technologies on data engineer job listings, SQL is a standardized programming language used to manage relational databases (not exclusively) and perform various operations on the data in them. Data Engineering using Spark SQL.
Programming Language
As a data engineer you'll be writing a lot of code to handle various business cases such as ETLs, data pipelines, etc. The de facto standard language for data engineering is Python (not to be confused with R or nim that are used for data science, they have no use in data engineering).
Python helps data engineers to build efficient data pipelines as many data engineering tools use Python in the backend. Moreover, various tools in the market are compatible with Python and allow data engineers to integrate them into their everyday tasks by simply learning Python.
Cloud Computing
Data engineers are expected to be able to process and handle data efficiently. Many companies prefer the cloud solutions to the on-premise ones. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the world's most comprehensive and broadly adopted cloud platform, offering over 200 fully featured services.
Data engineers need to meet various requirements to build data pipelines. This is where AWS data engineering tools come into the scenario. AWS data engineering tools make it easier for data engineers to build AWS data pipelines, manage data transfer, and ensure efficient data storage.
Shell Scripting
Unix machines are used everywhere these days and as a data engineer, they are something we interact with every single day. Understanding common shell tools and how to use them to manipulate data will increase your flexibility and speed when dealing with day to day data activities.
Git
Git is one of the skills that every software engineer needs to manage the code base efficiently. GitHub or any version control software is important for any software development projects, including those which are data driven. GitHub allows version control of your projects through Git.
VSCode
The VSCode provides rich functionalities, extensions (plugins), built-in Git, ability to run and debug code, and complete customization for the workspace. You can build, test, deploy, and monitor your data engineering applications and pipelines without leaving the application.
Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter Notebook is one of the most widely used tool in data engineering that use Python. This is due to the fact, that it is an ideal environment for developing reproducible data pipelines with Python. Colaboratory, or “Colab” for short, is a provide Jupyter-like environment on the cloud.
Relational Databases - Design & Architecture
RDBMS are the basic building blocks for any application data. A data engineer should know how to design and architect their structures, and learn about concepts that are related to them.
NoSQL Databases - Design & Architecture
NoSQL is a term for any non-relational database model: key-value, document, column, graph, and more. A basic acquaintance is required, but going deeper into any model depends on the job.
Columnar Databases
Column databases are a kind of nosql databases. They deserve their own section as they are essential for the data engineer as working with Big Data online (as opposed to offline batching) usually requires a columnar back-end.
Data Warehouses
Understand the concepts behind data warehouses and familiarize youself with common data warehouse solutions.
OLAP Data Modeling
OLAP (analytical) databases (used in data warehouses) data modeling concepts, modeling the data correctly is essential for a functioning data warehouse.
Data Lakes and Lakehouses
Batch Data Processing
Data processing using Python, SQL and Spark. Everyone should know how it works, but going deep into the details and operations are recommended only if necessary.
Stream Data Processing
Data processing on the fly. Suggested to get a good grasp of the subject and then dive deep into a specific tool like Kafka, Spark, Flink, etc.
Pipeline / Workflow Management
Scheduling tools for data processing. Airflow is considered to be the defacto standard, but any understanding of DAGs - directed acyclical graphs for tasks will be good.

